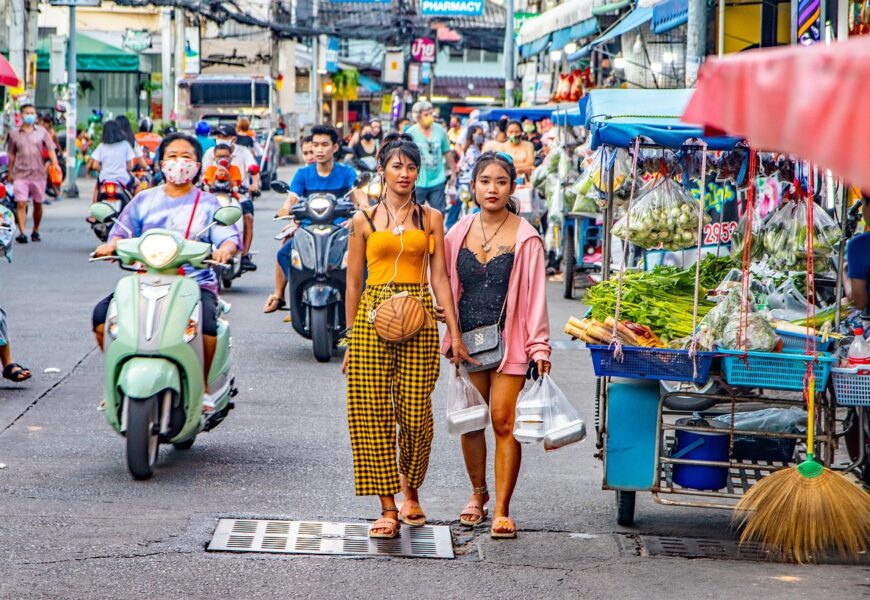
Thailand represents a fascinating cultural landscape where women play complex and evolving roles within society, balancing traditional expectations with modern aspirations. The experiences of Thai women reflect a nuanced interplay between historical traditions, cultural norms, economic opportunities, and global influences. From rural communities to urban centers, Thai women navigate intricate social dynamics that challenge simplistic external perceptions. Their stories encompass resilience, adaptation, and a profound commitment to family, education, and personal growth. Understanding the multifaceted nature of Thai women requires a deep exploration of historical context, contemporary challenges, and the remarkable ways they continue to shape their nation’s social and economic landscape.
Historical and Cultural Context
Historically, Thai society has maintained a distinctive approach to gender roles that differs significantly from Western perspectives. Buddhist traditions and indigenous cultural practices have long influenced women’s social positioning, creating a unique framework of respect and expectation. Unlike many patriarchal societies, Thai culture has traditionally afforded women considerable social mobility and economic participation. Women have been active participants in agricultural economies, small business enterprises, and familial decision-making processes. The matrilineal aspects of Thai social structures often provide women with substantial familial influence, challenging stereotypical assumptions about gender dynamics in Southeast Asian societies.
Traditional Thai cultural norms emphasize values of respect, harmony, and collective well-being. Women are often seen as crucial mediators within family units, responsible for maintaining social cohesion and emotional stability. These cultural expectations simultaneously provide opportunities and impose constraints, creating a complex landscape of personal and professional negotiation.
Economic Participation and Opportunities
Contemporary Thai women have made remarkable strides in economic participation across diverse sectors. Educational achievements have been particularly transformative, with women consistently outperforming men in higher education enrollment rates. Recent statistics indicate that approximately 55% of university graduates in Thailand are women, demonstrating significant intellectual and professional potential. Industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and entrepreneurship have witnessed increasing female leadership and representation.
The Thai government has implemented progressive policies supporting gender equality in workplace environments. Legal frameworks protecting women’s rights, promoting equal employment opportunities, and addressing workplace discrimination have contributed to expanding professional horizons. However, challenges persist, including wage disparities, limited representation in senior leadership positions, and lingering cultural biases that can impede career advancement.
Social Dynamics and Family Roles
Family remains a cornerstone of Thai women’s identities, with complex interpersonal relationships defining social experiences. While traditional expectations often emphasize maternal and caregiving responsibilities, contemporary Thai women are redefining these roles with increasing flexibility and personal agency. Urban centers like Bangkok showcase increasingly diverse family structures, with women pursuing professional careers while maintaining strong familial connections.
Intergenerational relationships carry significant weight in Thai society, with women often serving as critical links between traditional values and modern aspirations. The concept of ‘kreng jai’ – a nuanced cultural principle involving respect, consideration, and emotional restraint – profoundly influences social interactions and personal negotiations within familial and professional contexts.
Education and Personal Development
Educational opportunities have emerged as a powerful mechanism for personal transformation among Thai women. Universities and vocational institutions provide pathways for skill development, critical thinking, and professional preparation. International exchange programs, scholarships, and global educational networks have further expanded horizons, enabling women to gain sophisticated perspectives and competitive qualifications.
Digital technologies and global connectivity have dramatically expanded learning opportunities. Online education platforms, professional networking sites, and international collaborations offer unprecedented access to knowledge and professional development resources. These technological innovations have particularly benefited women in rural and economically marginalized communities, providing alternative pathways for personal and professional growth.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
Despite significant progress, Thai women continue to navigate complex social landscapes. Gender-based violence, workplace discrimination, and persistent cultural stereotypes remain challenging issues. Grassroots movements, legal reforms, and increasing social awareness have contributed to addressing these systemic challenges, promoting more inclusive and equitable societal structures.
Emerging generations of Thai women demonstrate remarkable resilience, creativity, and determination. They are actively reshaping societal narratives, challenging traditional limitations, and creating innovative pathways for personal and collective empowerment. Their experiences represent a dynamic intersection of cultural heritage and contemporary global perspectives.
In conclusion, Thai women embody a powerful narrative of adaptation, resilience, and continuous transformation. Their journeys reflect broader societal shifts, challenging simplistic external perceptions and demonstrating remarkable capacity for personal and collective growth. By honoring traditional values while embracing progressive opportunities, Thai women are actively constructing multifaceted identities that transcend historical limitations. Their ongoing contributions across economic, social, and cultural domains underscore the importance of recognizing women’s experiences as fundamental to understanding complex societal dynamics.